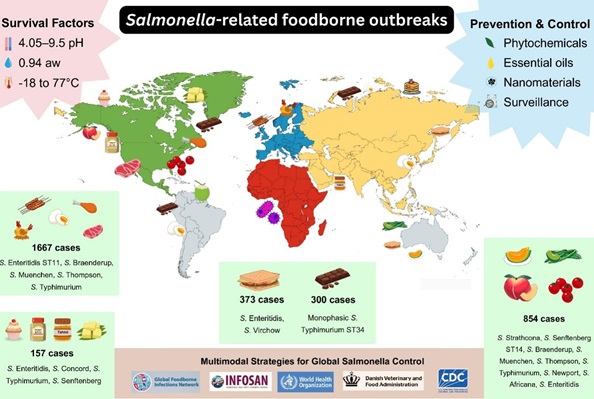
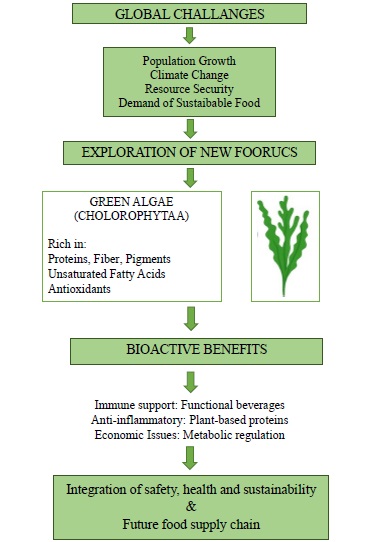
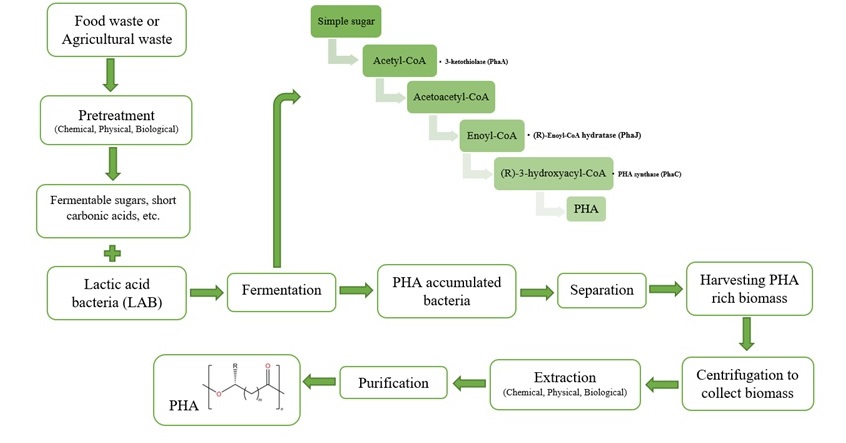
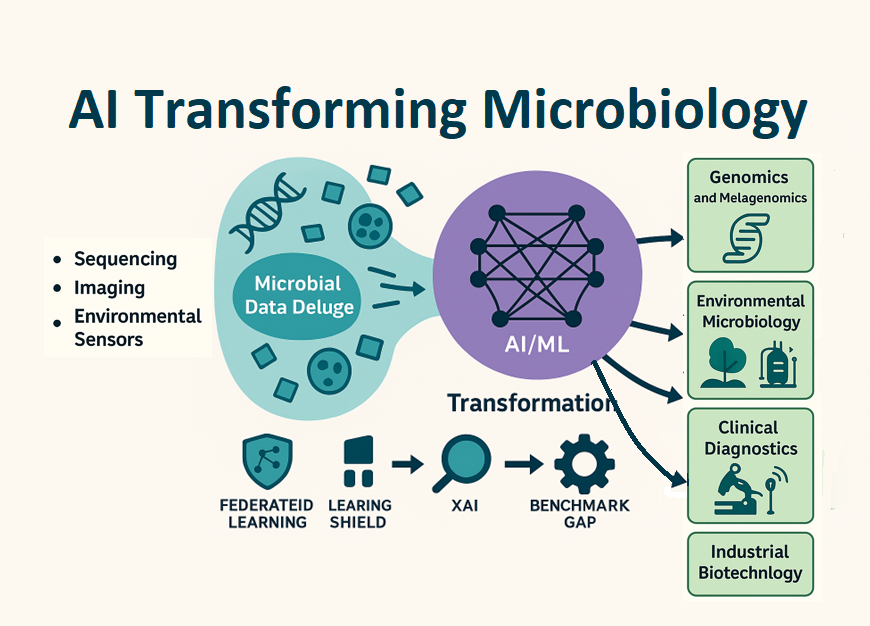
About the Journal
innovations shaping tomorrow's solutions, bridging biology and technology for a sustainable future, convergence of science, society, and sustainability, cutting-edge research in biotechnology and bioengineering, decoding life through advanced biotechnological approaches, engineering nature for health and environment
Current Issue
Vol. 2 No. 1 (2025): Serial Number 2

Published:
2025-01-01