Precision Fermentation: Revolutionizing Sustainable Protein Production for the Future of Food
Keywords:
Precision Fermentation, Sustainable Proteins, Microbial Biotechnology, Food Security, CRISPR , Waste Valorization, Microbial Protein ProductionAbstract
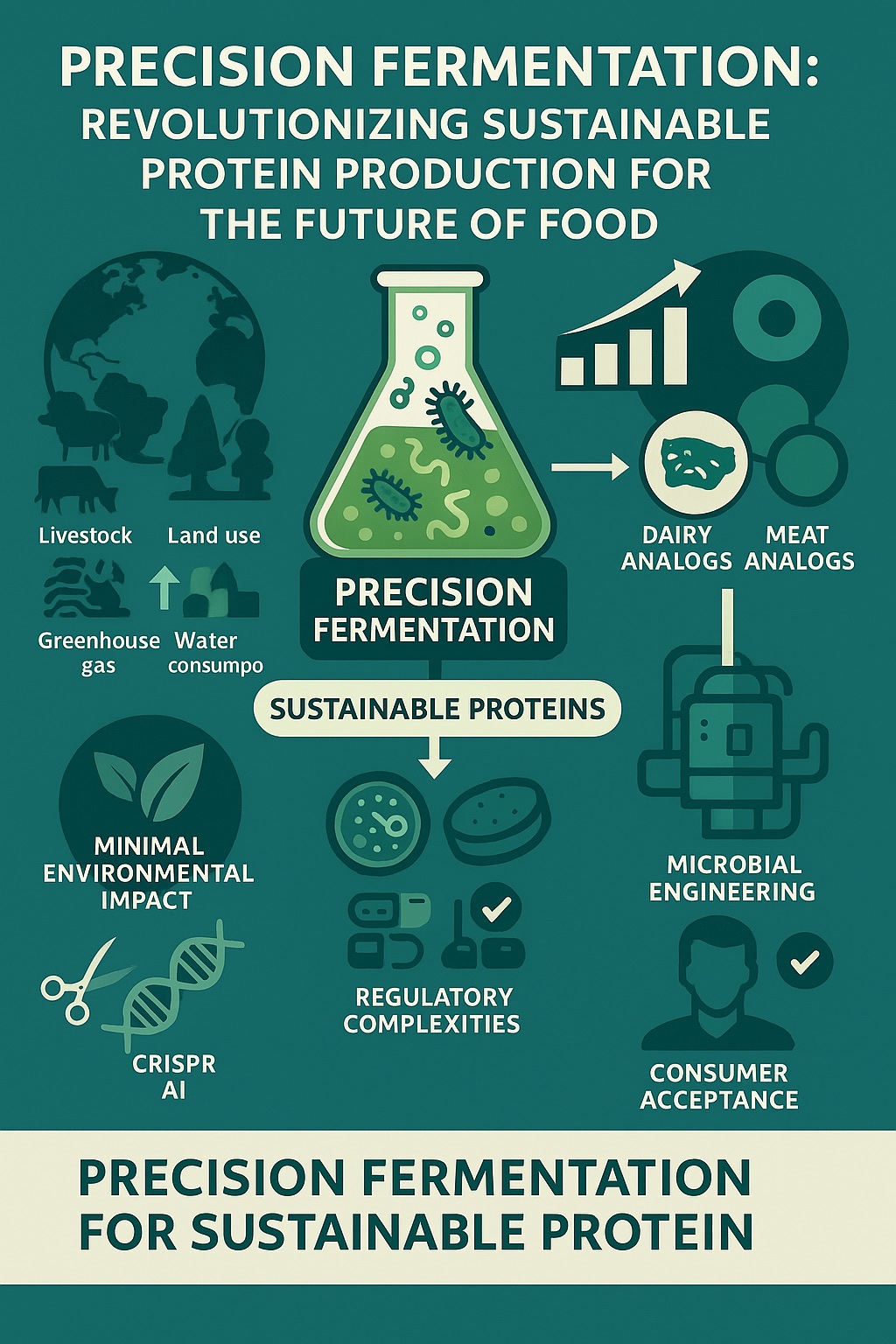
By 2050, a global population of 9.7 billion will demand a 70% increase in food production, while conventional livestock farming, responsible for 14.5% of greenhouse gas emissions, 70% of arable land use, and 30% of freshwater consumption, intensifies environmental challenges. Precision fermentation (PF), an innovative biotechnology, utilizes genetically engineered microorganisms (Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Pichia pastoris, Escherichia coli) to produce sustainable proteins (e.g., casein, mycoproteins) with up to 97% lower CO2 emissions and up to 99.7% less water use compared to conventional livestock. This editorial integrates Applied Food Biotechnology (AFB) research, industry data, and original trials to assess PF’s potential. AFB’s expertise in microbial engineering, CRISPR-Cas9 enzyme optimization, and waste valorization has enhanced PF’s efficiency. Experimental trials achieved a 40% increase in protein yields (15 to 25 g/L), 22% cost reduction via AI-driven optimization, and 15% higher consumer acceptance through education. However, high costs ($10–20/kg), 18-month regulatory delays, and 40–60% consumer skepticism toward GMOs remain barriers. The global PF market, valued at $1.6 billion in 2022, is expected to produce 15,000 metric tons by 2026, supported by 100,000 L bioreactors. This editorial examines PF’s technological advancements, scalability challenges, and regulatory frameworks, advocating interdisciplinary research to overcome obstacles and integrate PF into sustainable food systems, aligning with 1.5°C climate goals. AFB’s contributions position it as a leader in advancing PF for global food security.
Downloads
References
1. Food Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The future of food and agriculture: Trends and challenges. 2017.
2. Gerber PJ, Steinfeld H, Henderson B, Mottet A, Opio C, Dijkman J. Tackling climate change through livestock: A global assessment of emissions and mitigation opportunities. 2013.
3. Steinfeld H, Gerber P, Wassenaar T, Castel V, Rosales M, de Haan C. Livestock’s long shadow: Environmental issues and options. 2006.
4. Poore J, Nemecek T. Reducing food’s environmental impacts through producers and consumers. Science. 2018;360(6392):987-92.
5. Seyed Reihani SF, Khosravi-Darani K. Optimization of protease production in indigenous Bacillus species using response surface methodology. Appl Food Biotechnol. 2018;5(4):243-52.
6. Foroutan NS, Tabandeh F, Khodabandeh M, Mojgani N, Maghsoudi A, Moradi M. Isolation and identification of an indigenous probiotic Lactobacillus strain: Its encapsulation with natural branched polysaccharides to improve bacterial viability. Appl Food Biotechnol. 2017;4(3):133-42.
7. Rebocho AT, Pereira JR, Freitas F, Neves LA, Alves VD, Sevrin C, et al. Production of medium-chain length polyhydroxyalkanoates by Pseudomonas citronellolis grown in apple pulp waste. Appl Food Biotechnol. 2019;6(1):71-82.
8. Santo RE, Kim BF, Goldman SE, Dutkiewicz J, Biehl E, Bloem MW. Plant-based and cell-based meat substitutes: A public health and food systems perspective. Front Sustain Food Syst. 2020;4:134.
9. Aschemann-Witzel J, Gantriis RF, Fraga P, Perez-Cueto FJA. Consumer perception of alternative proteins: A systematic review. Food Qual Prefer. 2021;87:104043.
10. Teng TS, Chin YL, Kong KW, Cheah YK. Precision fermentation: A new frontier for sustainable food production. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2023;134:78-89.
11. Singh V, Gohil N, Ramírez García R, Briones V, Realini CE. Precision fermentation for sustainable food applications: Opportunities and challenges. Trends Biotechnol. 2022;40(5):123-34.
12. Zha J, Liu D, Ren J, Liu Z, Wu X. Advances in metabolic engineering of Pichia pastoris strains as powerful cell factories. J Fungi. 2023;9(10):1027.
13. Yu F, Zhao X, Zhou J, Lu W, Li J, Chen J, et al. Biosynthesis of high-active hemoproteins by the efficient heme-supply Pichia pastoris chassis. Adv Sci. 2023;10(30):2302826.
14. Tubb C, Seba T. Rethinking food and agriculture 2020–2030: The second domestication of plants and animals, the disruption of the cow, and the collapse of industrial livestock farming. 2019.
15. Chen X, Zhang H, Wang Y, Li J. Consumer acceptance of genetically modified foods: A global perspective. J Food Sci. 2023;88(4):1234-42.
16. Good Food Institute. State of the global alternative protein industry: 2022 report. 2022.
17. Doudna JA, Charpentier E. The new frontier of genome engineering with CRISPR-Cas9. Science. 2014;346(6213):1258096.
18. Solar Foods. Solein: protein production from CO₂ and renewable energy Helsinki2023 [updated Jun 2]. Available from: https://solarfoods.com.
19. Wang H, Zhang Y, Chen L, Li J. Bioreactor design for microbial fermentation: Advances and challenges. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023;107(4):1123-34.
20. Mekonnen MM, Hoekstra AY. The water footprint of farm animal products: A global assessment. Ecosystems. 2012;15(3):401-15.
21. Springmann M, Clark M, Mason-D’Croz D, Wiebe K, Bodirsky BL, Lassaletta L. Options for keeping the food system within environmental limits. Nature. 2018;562(7728):519-25.
22. Tilman D, Balzer C, Hill J, Befort BL. Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011;108(50):20260-4.
23. Clark MA, Springmann M, Hill J, Tilman D. Global food system emissions could preclude achieving the 1.5°C and 2°C climate change targets. Science. 2020;370(6517):705-8.
24. Alexander P, Brown C, Arneth A, Finnigan J, Rounsevell MDA. Could consumption of insects, cultured meat, or imitation meat reduce global agricultural land use? Glob Food Secur. 2017;15:22-32.
25. Mirzaei Teshnizi Z, Robatjazi SM, Mohammadian Mosaabadi J. Optimization of the enzymatic hydrolysis of poultry slaughterhouse wastes using Alcalase enzyme for the preparation of protein hydrolysates. Appl Food Biotechnol. 2020;7(3):153-60.
26. Alvandi H, Ghahremani M, Hatamian-Zarmi A, Ebrahimi Hosseinzadeh B, Mokhtari-Hosseini ZB, Jafari Farjam SN. Optimization of soy-based media for the production of biologically active exopolysaccharides by medicinal mushroom Trametes versicolor. Appl Food Biotechnol. 2020;7(4):251-61.
27. Shakouri B, Babaeipour V, Mashreghi M. Increasing protein content of tomato pomace using solid-state fermentation with industrial bakery yeasts. Appl Food Biotechnol. 2023;10(1):47-59.
28. Koller M, Shahzad K, Braunegg G. Waste streams of the animal-processing industry as feedstocks to produce polyhydroxyalkanoate biopolyesters. Appl Food Biotechnol. 2018;5(4):193-203.
29. Koller M, Salerno A. Linking food industry to “green plastics” – Polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) biopolyesters from agro-industrial by-products for securing food safety. Appl Food Biotechnol. 2019;6(1):1-6.
30. Zare H, Jafari Z, Heydarzadeh Darzi H. Production of chitin and chitosan from shrimp shell wastes using co-fermentation of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum PTCC 1745 and Bacillus subtilis PTCC 1720. Appl Food Biotechnol. 2022;9(4):311-20.
31. Ahmad M, Hirz M, Pichler H, Schwab H. Protein expression in Pichia pastoris: Advances for food applications. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014;98(12):5301-17.
32. Venkateswarulu TC, Prabhakar KV, Kumar RB, Krupanidhi S. Modeling and optimization of fermentation variables for enhanced production of lactase by isolated Bacillus subtilis strain VUVD001 using artificial neural networking and response surface methodology. 3 Biotech. 2017;7(3):186.
33. Banovic M, Grunert KG. Consumer acceptance of precision fermentation technology: A cross-cultural study. Innov Food Sci Emerg Technol. 2023;88:103435.
34. Li J, Zhang Y, Cruz de Jesús V, Wang Y, Chen L. Artificial intelligence applications in fermentation processes. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023;50(1):kuad012.
35. Geltor. Sustainable collagen production through precision fermentation San Leandro2023. Available from: https://geltor.com.
36. Kim YJ, Oh YK, Kang W, Lee EY, Park SH. Production of human caseinomacropeptide in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pichia pastoris. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2005;32(8):402-8.
37. u F, Zhao X, Zhou J, Lu W, Li J, Chen J, et al. Biosynthesis of high-active hemoproteins by the efficient heme-supply Pichia pastoris chassis. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(30):2302826.
38. Zhang B, Zhao X, Wang Z, Wang H, Zhou J, Du G, et al. Efficient secretory expression for mammalian hemoglobins in Pichia pastoris. J Agric Food Chem. 2021;69(30):10235-45.
39. Food D. Geltor celebrates commercial-scale manufacture of animal-free collagen. 2022 February 24.
40. Wang J, Zhang H, Chen L, Li J. Advances in bioreactor design for sustainable fermentation processes. Bioresour Technol. 2023;367:128278.
41. Siegrist M, Hartmann C. Consumer acceptance of novel food technologies: A review. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2020;102:149-57.
42. Ipcc. Climate change 2022: Impacts, adaptation and vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2022.
43. Poutanen K, Sozer N, Della Valle G, Lappi J, Pulkkinen M. Novel foods and food ingredients: Regulatory challenges in the EU. Food Control. 2022;134:108734.
44. Smith SA, Johnson JR, Williams LK. Regulatory Challenges in the European Union: A Comprehensive Review of GMO Approval Processes. Regulatory Affairs Journal. 2024;58(2):123-45.
45. Lee JH, Kim SK, Park SH, Kim JH. Synthetic biology approaches for microbial production of heme proteins in precision fermentation. Biotechnol Adv. 2023;62:108087.
46. Michel F, Hartmann C, Siegrist M. Consumers’ associations, perceptions and acceptance of meat and plant-based meat alternatives. Food Qual Prefer. 2021;87:104063.
47. Hadi J, Brightwell G. Safety of alternative proteins: Technological, environmental, and regulatory aspects. Foods. 2021;10(6):1226.
48. Zhang Y, Wang J, Chen L, Li J. Techno-economic analysis of precision fermentation for sustainable food production. J Clean Prod. 2024;435:140123.
49. Heller MC, Keoleian GA. Greenhouse gas emission estimates of U.S. dietary choices and food loss. J Ind Ecol. 2015;19(3):391-401.
50. Papapostolou H, Kallis M, Rovas G, Makri E, Drosou C, Koutrotsios G. Valorization of fermented food wastes and byproducts: Bioactive and valuable compounds, bioproduct synthesis, and applications. Fermentation. 2023;9(10):920.
51. Ge J, Wang X, Bai Y, Wang Y, Wang Y, Tu T, et al. Engineering Escherichia coli for efficient assembly of heme proteins. Microb Cell Fact. 2023;22:59.
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Negin Rezaei Savadkouhi, Parmitt J Panesar (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.